
India has Officially Entered the Super 40 Club- Dholavira विश्व धरोहर में शामिल

Dholavira: A Harrapan City, Gujarat
The ancient city of Dholavira is one of the most remarkable and well-preserved urban settlements in South Asia dating from the 3rd to mid-2nd millennium BCE (Before Common Era). Discovered in 1968, the site is set apart by its unique characteristics, such as its water management system, multi-layered defensive mechanisms, extensive use of stone in construction and special burial structures. Of note is also the art associated with the city – artefacts of various kinds such as copper, shell, stone, jewellecus on, ni-precious stones, terracotta, gold, ivory have been found at the site. In addition, the interregional trade links who hollavorh Dholavira, have also been acknowledged as contributing to the shared heritage of humanity.
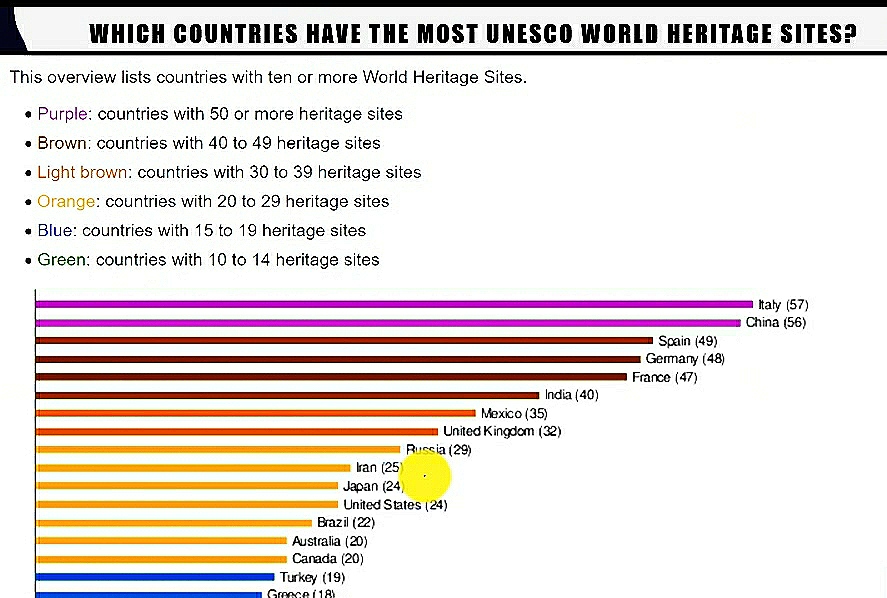
UNESCO published its first list of protected places in 1978. From 1978 to 2014 India got 30 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, From 2014 to 2021 India got 10 sites recognised
DHOLAVIRA
Dholavira is an archaeological site at Khadirbet in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch District, in the state of Gujarat in western India, which has taken its name from a modern-day village I kilometre (0.62 mi) south of it.
It is located on Khadir bet island in the Kutch Desert Wildlife Sanctuary in the Great Rann of Kutch.
The site was thought to be occupied from c.2650 BCE, declining slowly after about 2100 BCE, and to have been briefly abandoned then reoccupied until c. 1450 BCE
Dholavira is the most spectacular IVC site in India and the fifth largest in the subcontinent in terms of areal coverage
(Mohenjo Daro 250 hectare (Ha), Harappa 150 Ha, Rakhigarhi 80-105 Ha, Ganeriwala 81 Ha and Dholavira 70 Ha).
QUESTION FOR YOU ALL
India’s first UNESCO World Heritage Site was
the..
A. Ajanta Caves
B. Ellora Caves
C. Agra Fort
D. Taj Mahal
ANSWER – A
Maharashtra
The Ajanta Caves are Buddhists caves built in two phases. The first, was from the reign of Emperor Ashoka. The second, further additions were made during the 5th and 6th centuries AD of the Gupta period. The caves depict richly decorated fresco paintings, reminiscent of the





